Network configuration management for secure and optimized networks

A single misconfiguration can bring down an entire network. It might block someone from logging in, expose private data, or break secure VPN tunnels between offices. Yet, with so many devices and settings to manage, keeping everything in sync can be tricky for even the most experienced teams.
Network configuration management (NCM) helps teams keep all of that under control. In this guide, we’ll explain what NCM is, how it works, and why it’s essential for keeping business networks secure, consistent, and resilient.
What is network configuration management (NCM)?
NCM is the process of keeping all your network device settings organized, consistent, and backed up. It ensures the rules that guide how routers, switches, firewalls, and VPN gateways connect and communicate are clearly documented, follow security policies, and stay consistent across the network.
NCM also includes tracking every change in settings and alerting administrators when something unexpected happens, like a router update that disrupts traffic or a firewall rule that blocks the wrong ports. With backups in place, teams can quickly roll back to a working version and restore service with minimal downtime.
To handle all this efficiently, teams often rely on dedicated NCM tools, which automate repetitive work like configuration backups, version tracking, and compliance checks across large networks. They also centralize management, making it easier to push updates or enforce policies on several devices at once. This level of automation helps keep configurations consistent and secure, without the need to manually adjust every device.
Why configuration management is critical for security
NCM is critical because it reduces the risk of human error and misconfigurations, which are two of the biggest causes of security breaches. Missteps like leaving a firewall open, using default passwords, or skipping security patches create easy entry points for attackers, who often scan networks specifically to exploit these vulnerabilities.
Common misconfigurations that weaken security include:
- Default credentials: Factory-set usernames and passwords are widely known and can be easy to exploit.
- Open or unused ports: Accessible ports can expose internal services to the internet.
- Unpatched systems: Delaying software updates can leave devices open to known vulnerabilities.

- Excessive permissions: Granting more access than necessary increases the risk of misuse or data leaks.
- Insecure APIs: Interfaces without authentication can expose sensitive data or internal systems.
- Disabled encryption: Allowing unencrypted connections can let attackers intercept traffic, such as HTTP instead of HTTPS.
Real-life examples: Configuration gone wrong
In 2019, Capital One, one of the largest credit card issuers in the U.S., suffered a major data breach that exposed the personal information of over 100 million customers in the U.S. and 6 million in Canada. The attacker gained access through a misconfigured web application firewall in the company’s cloud environment hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
The exposed data included sensitive personal information, such as names, contact information, dates of birth, and self-reported income, as well as customer account data, such as credit scores, credit limits, balances, payment history, and contact information. Additionally, about 140,000 customer Social Security numbers were stolen.
In 2020, a Microsoft Bing mobile app Elasticsearch server was left publicly accessible without a password for several days. The issue stemmed from a simple configuration error that allowed external access to a backend system intended to remain internal.
This exposed roughly 100 million log records to anyone who discovered the endpoint. The data included search queries, device details, and in some cases GPS coordinates and other diagnostic information.
Key functions of network configuration management
NCM involves several key steps to help keep networks secure and reliable. The most important include identifying devices, organizing backup, managing network changes, and ensuring compliance.
Device discovery and inventory management
The first step in configuration management is knowing what’s on the network. You can use discovery tools to scan connected routers, switches, firewalls, and VPN gateways and build a detailed inventory of devices. The inventory typically shows each one’s type, firmware version, IP address, and configuration details. From there, network admins can create and visualize the network topology to see how everything connects.
This gives administrators full visibility and helps teams spot outdated hardware, duplicate configurations, or unauthorized devices that shouldn’t be there. With that insight, they can plan updates, apply security checks, and make sure every device meets current standards.
Configuration backup and quick restore
Backing up device configurations is an important part of rollback configuration, ensuring there’s always a safe version to fall back on if something triggers downtime. An effective configuration management system automatically saves the current setup of routers, switches, firewalls, and VPN gateways so you have a secure version to fall back on.
When something breaks, administrators can compare versions, identify what changed, and restore the last working configuration within minutes.
Managing changes across your network
Every change to a network configuration carries risk. A small adjustment to routing rules, firewall policies, or VPN parameters can have unexpected effects elsewhere in the system. Without proper tracking, it’s hard to know who made a change, when it happened, or why something stopped working.
Practicing effective change management means creating a clear record of every modification, so administrators can see what changed, compare it against previous versions, and roll back if needed. These logs also show unauthorized edits, such as firewall rules that open restricted ports or changes to VPN access lists that bypass authentication.
Staying compliant with security standards
Most organizations need to follow specific security and privacy standards to protect sensitive data and meet regulatory obligations. Automated network configuration can support compliance management with these regulations by flagging potential issues early.
CIS policy support
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) is a non-profit organization that provides widely recognized benchmarks that define how network devices should be securely configured. These guidelines cover measures such as disabling unused services, enforcing strong authentication, restricting management access, and using modern encryption standards. For example, local usernames and passwords should be defined, and remote administration should only be allowed through trusted networks or VPNs.
PCI, SOX, and HIPAA coverage
Different industries face different compliance pressures. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requires you to reset passwords every 90 days if using single-factor authentication, review system configurations, and protect cardholder data with strong cryptography.
In the U.S., the Sarbanes–Oxley Act (SOX) sets requirements for financial reporting and internal controls. Implementing strong security measures, like controlling login attempts and access to financial systems, helps organizations comply with SOX. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is more specific to healthcare, focusing on keeping patient information private by monitoring traffic and restricting risky protocols.
Whichever regulation it is, NCM helps support compliance by tracking who changed what, when it happened, and whether the system still meets requirements.
GDPR compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict rules on how organizations handle and protect personal data. It requires strong technical and organizational measures to prevent unauthorized access, data leaks, and misuse of information. For example, using encryption, managing access control, and carrying out regular security audits.
NCM can support compliance with GDPR by checking that systems handling personal data are set up securely. It can verify that routers, VPN gateways, and firewalls use approved encryption standards, and that logs or backups don’t store personal information where they shouldn’t.
Why network configuration matters for VPN security
A VPN is only as secure as the network it runs on. It relies on networks, switches, firewalls, and Domain Name System (DNS) servers underneath to work correctly.
Avoiding DNS and IP leaks via proper configurations
A VPN protects all of your internet traffic in an encrypted tunnel. If DNS or routing settings aren’t configured correctly, some of that data can bypass the VPN tunnel entirely. This might reveal your real IP address or send DNS queries to public servers instead of through the VPN.
Proper network configuration closes those gaps, making sure everything is routed through the encrypted tunnel. That includes using the VPN’s own DNS servers instead of public ones, blocking any external DNS requests, and setting routes so apps can’t bypass the tunnel. All traffic traveling over the network goes through the encrypted VPN tunnel, safely concealing it from others.
Ensuring consistent security across devices
A VPN is most effective when every device on the network follows the same security rules. If one router or gateway uses outdated firmware or weaker encryption, it can become the weak link that compromises the rest.
Configuration management keeps those devices in sync, applying the same standards for encryption, authentication, and access, including strong network security keys. This ensures that no matter where someone connects from, the same level of protection applies across the entire network.
Boosting VPN speed through optimized network paths
NCM helps ensure that routing rules, firewall settings, and VPN parameters are consistent and correctly applied across all devices. While NCM itself doesn’t dynamically optimize network paths in real time, it supports VPN performance by:
- Enforcing correct routing and DNS settings so traffic flows through intended paths without unnecessary detours.
- Ensuring all devices use updated firmware and consistent configurations, preventing misconfigurations that could slow down connections.
NCM is used to deploy and manage the configuration of routing protocols and other optimization tools, which are responsible for the dynamic optimization of network paths. By maintaining a stable, predictable network baseline, NCM ensures these protocols and tools function as intended.
Preventing human errors with automated scripts
Network configuration changes are often made manually, and that’s where mistakes happen most easily. A single missing command or incorrect IP rule can block VPN traffic or take systems offline. Automation reduces that risk by rolling out updates the same way every time and checking that each change matches what’s expected. This helps keep VPN connections stable and minimizes downtime.
Why versioning is essential for VPN stability
VPN connections depend on both sides of a tunnel using identical settings. If one device updates its encryption suite, key exchange method, or IP range and the other doesn’t, the tunnel can fail instantly.
Versioning keeps a copy of each previous configuration so you can restore the exact setup that worked before the change. It also helps test new configurations safely. For example, when rolling out stronger encryption or new routing rules, you can compare how the new version performs against the last stable one. If latency increases or authentication starts failing, you can revert to the earlier configuration without rebuilding the tunnel from scratch.
How to implement configuration management in your network
Setting up configuration management doesn’t have to be complicated. It starts with a clear record of how your network is built and the tools you’ll use to keep it consistent.
Basic setup for small remote teams
1. Define your configuration strategy
Decide how configurations will be created, reviewed, and updated. Agree on which devices you will track, who approves changes, and how updates are recorded. That way, everyone is clear on who’s doing what, and it helps keep configuration consistent across your network.
2. Identify key devices and settings
List every device that needs attention, such as routers, firewalls, VPN gateways, and switches. As you go, create a visual network map to show how everything connects. Give each one a clear name and record details like software version, encryption settings, and access controls, so it’s easier to spot what’s missing or out of date.
3. Establish a secure baseline
A baseline is your snapshot of a working, approved setup. It includes current configurations, firmware versions, and policies for encryption and routing. Comparing future changes against this baseline helps catch unauthorized edits or mistakes before they cause issues.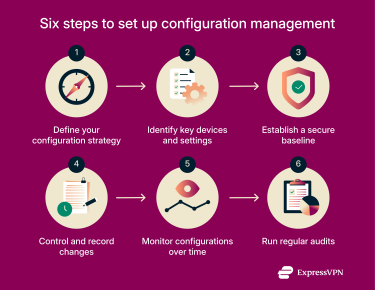
4. Control and record changes
Untracked changes are one of the main causes of outages. Review and approve updates before applying them, and log what changed, who did it, and why. Good records make it simple to audit or roll back if something fails.
5. Monitor configurations over time
Over time, small, unnoticed changes (known as configuration drift) can weaken security or disrupt network performance. Regular reviews help confirm that devices still match the approved baseline configuration.
6. Run regular audits
Audits make sure the network still matches its approved configuration. They help uncover outdated rules, old firmware, or unauthorized changes that could slip through unnoticed.
How to manage rollbacks effectively
A rollback lets you quickly recover when an update or configuration goes wrong. To make it reliable:
- Keep verified backups: Store and update working configurations regularly so they reflect your current setup.
- Label versions clearly: Use clear names or timestamps to avoid confusion during recovery.
- Test restores: Make sure backups actually work and can be restored fast.
- Automate when possible: Automation saves time and reduces human error.
Choosing the right configuration management tools
A good configuration management tool should make it easy to keep every device secure and consistent. The right choice depends on your network’s size, the number of devices you manage, and how closely you need to monitor VPN connections.
Must-have features for VPN-ready environments
Configuration management tools should support the key tasks that keep VPNs stable and secure:
- Automated backups and version control: Captures every device configuration and lets you restore it quickly if something fails.
- Change tracking and alerts: Sends notifications when routers, firewalls, or VPN gateways are modified without approval.
- Configuration templates: Enforces consistent policies for VPN tunnels, encryption settings, and access control across devices.
- Multi-vendor compatibility: Works with hardware and software from different manufacturers to simplify hybrid or complex networks.
Comparing open-source vs. enterprise tools
Open-source tools such as RANCID and Oxidized offer flexibility and strong automation. This makes them ideal for smaller teams that want full control over their setup, because you can write scripts, set up custom backup schedules, and control exactly how to deploy VPN or firewall policies.
The trade-off is that these tools need more maintenance and technical knowledge to configure. They also depend on community updates for patches and bug fixes, which can leave security issues unresolved for longer if they’re not closely monitored. This can potentially expose your network to vulnerabilities.
Enterprise tools like SolarWinds, ManageEngine, and Cisco DNA Center come with built-in policy enforcement, detailed reporting, and dedicated support. They’re designed for larger networks, where several administrators work simultaneously and mistakes have the potential to spread quickly.
They also have centralized dashboards that let teams roll out updates to hundreds of devices at the same time, verify that VPN gateways use the same encryption and access rules, and produce compliance reports without manual checks. However, enterprise tools are less flexible than open-source solutions, with predefined policies.
| Open-source tools | Enterprise tools | |
| Setup and customization | Highly flexible, with manual setup | Easier setup with predefined policies |
| Maintenance | Needs technical maintenance | Managed by a third party with support |
| Scale | Best for smaller networks | Best for larger networks |
| Example tools | RANCID, Oxidized | SolarWinds, ManageEngine, Cisco DNA Center |
The best option depends on your environment and resources. Smaller, technically skilled teams may prefer open-source flexibility, while bigger networks often benefit from the reliability and oversight of enterprise systems.
Cloud-based vs. on-premise solutions
Configuration management tools can run either in the cloud or on your own infrastructure. Which one you use depends on how your network is built and how much control you want over data and access.
Cloud-based configuration management
Cloud-based tools are hosted by a provider and accessed through a web interface. They make it easier to manage devices across multiple offices or remote sites, since administrators can log in from anywhere and see the configuration status in real time. Updates, backups, and version control for configurations happen automatically, which reduces local maintenance work.
However, because these tools depend on internet connectivity, they must be integrated carefully with your organization’s security policies. It’s important to verify where configuration data is stored, who can access it, and how it’s encrypted during transfer and at rest.
On-premise configuration management
On-premise tools are installed and run within your own network. They give organizations full control over configuration data, which is often required for compliance or privacy reasons. This setup can reduce exposure to external threats, but it also puts the responsibility for updates, backups, and access control on your internal team.
On-premise systems tend to suit organizations with dedicated IT staff, strict data handling rules, or limited internet access between sites. They provide stronger control but require more maintenance and infrastructure support.
| Cloud-based configuration management | On-premise configuration management | |
| Deployment | Hosted by a provider and accessed through a browser | Installed and managed within your own network |
| Accessibility | Allows administrators to view and adjust configurations remotely | Managed locally within the network environment |
| Maintenance | Backups and updates handled automatically | Updates, security patches, and storage handled by internal teams |
| Data control | Configuration data stored by the provider | Full control over where and how data is stored |
| Security considerations | Must align with existing security and privacy policies | Offers stronger isolation from third-party systems |
| Suitability | Best for distributed teams or smaller IT departments | Best for organizations with strict compliance or privacy requirements |
Hybrid approaches
Many teams now use a hybrid model that combines both options. For example, a company might use cloud-based dashboards for configuration monitoring and automation but store sensitive configuration backups locally. When combined, administrators can have remote visibility and flexibility without giving up control of critical data. Network configuration management (NCM) keeps VPN connections secure by ensuring all devices use the same approved settings. It prevents errors that could expose data, such as weak encryption or incorrect routing rules. NCM also allows teams to track changes, detect unauthorized updates, and quickly restore safe configurations if something goes wrong. Automation is generally more reliable than manual setup, especially in larger or fast-changing networks. Automated tools can apply updates consistently, back up configurations, and flag issues before they cause downtime. Manual setup might work for small teams, but it’s easier for mistakes or outdated settings to slip through. A single misconfiguration can break VPN tunnels, expose IP addresses, or leave parts of your network unprotected. It can also block legitimate traffic or disconnect users entirely. With proper configuration management, errors can be detected early and rolled back to a working version within minutes. Use a centralized configuration management system to apply, track, and verify settings across all routers, firewalls, and VPN gateways. This ensures every device follows the same policies for encryption, access, and authentication. Centralized control also makes updates faster and troubleshooting easier when something changes. Tools like ManageEngine Network Configuration Manager, SolarWinds NCM, and RANCID can automatically back up device configurations. They save secure copies whenever changes occur so you can restore a working version instantly if an update fails or a device goes offline. For smaller teams, open-source options like Oxidized also provide simple, reliable backup management. Configuration hygiene means keeping your network setup clean and consistent by removing outdated rules, accounts, and settings. Over time, unused configurations can pile up, slowing performance and leaving security gaps attackers could exploit. Regular cleanups (like auditing firewalls, deleting old credentials, and retiring legacy settings) help keep the network secure, reliable, and easier to manage.FAQ: Common questions about network configuration management
What is the role of NCM in VPN security?
Do I need manual setup, or is automation better?
What happens if my network configuration is wrong?
How do I manage configs across multiple devices?
Which tools are best for VPN configuration backup?
What is configuration hygiene, and why does it matter?
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN